CLARITEK Drops
ក្រុមហ៊ុនផលិតឱសថ:
getz pharma, USA
ក្រុមហ៊ុនចែកចាយឱសថនៅប្រទេសកម្ពុជា:
ALLIANCE PHARMA CAMBODGE
- សារធាតុសកម្ម
- ប្រសិទ្ធិភាពព្យាបាល និង កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់
- ហាមប្រើ
- ផលរំខាន
- អន្តរប្រតិកម្ម
- ស្ត្រីមានផ្ទៃពោះ និង ស្ត្រីបំបៅដោះកូន
- ការប្រុងប្រយ័ត្នជាពិសេស
- សកម្មភាពឱសថ បរិយាយប័ណ្ណឱសថ
-
សារធាតុសកម្ម
Clarithromycin 125mg/5mL
-
ប្រសិទ្ធិភាពព្យាបាល និង កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់
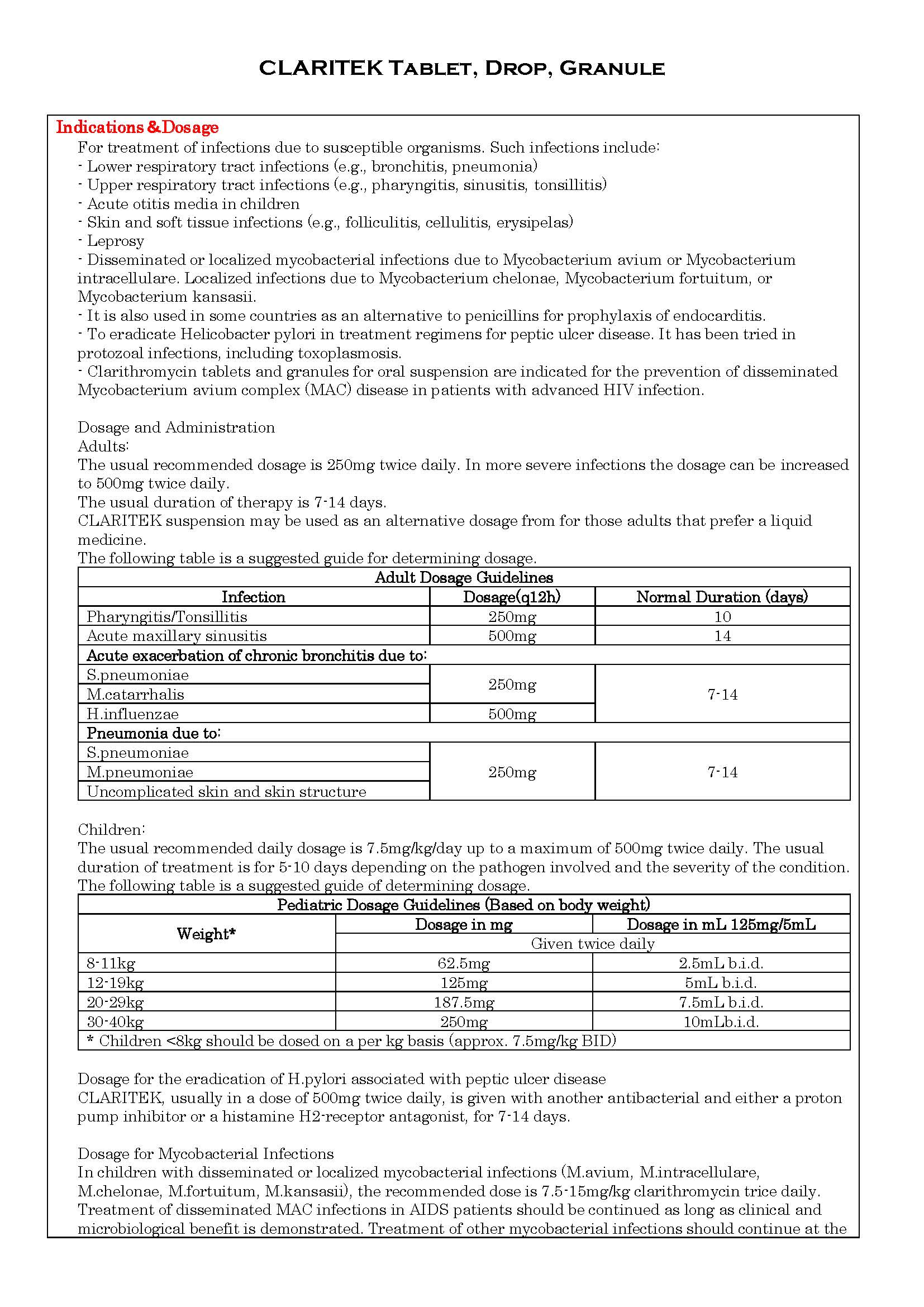
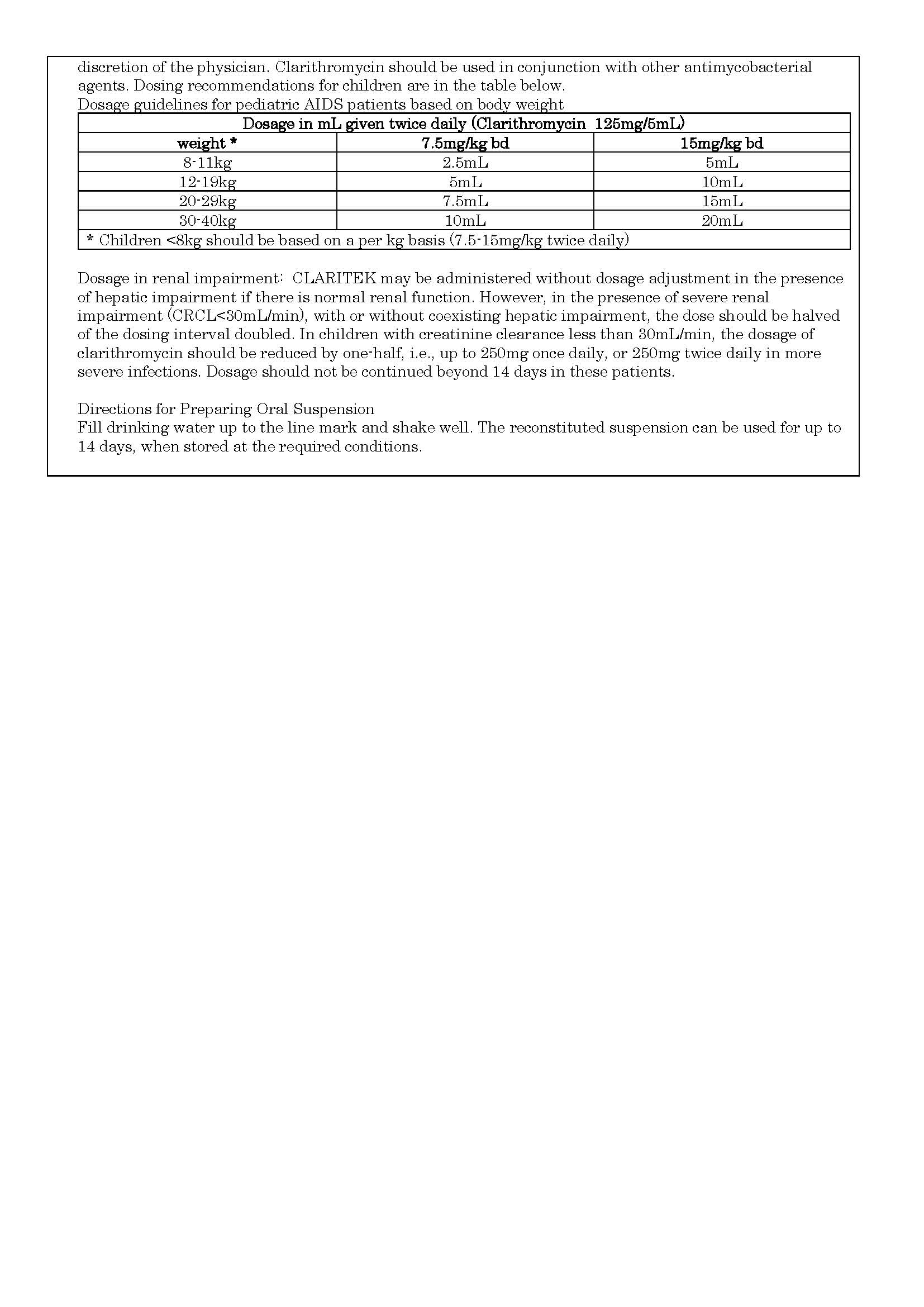
-
ហាមប្រើ
Clarithromycin is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to macrolide antibiotic drugs.
Concomitant administration of clarithromycin with any of the following medicines is contraindicated: astemizole, cisapride, pimozide and terfenadine.
-
ផលរំខាន
The most frequently reported side effects in clinical studies were gastrointestinal related, i.e. nausea, dyspepsia, abdominal pain, vomiting and diarrhea. Other reported side effects include headache, taste perversion and transient elevations of liver enzymes.
Headache and rashes from mild skin eruptions to, rarely, Stevens-Johnson syndrome has occurred. There have also been reports of transient CNS effects such as anxiety, dizziness, insomnia, hallucinations, and confusion.
Other adverse effects include hypoglycemia and thrombocytopenia, interstitial nephritis, renal failure, hearing loss, glossitis, stomatitis, oral monilia and tongue discoloration have been reported with clarithromycin therapy.
Adverse laboratory changes. Abnormal liver function test results may occur following therapy with clarithromycin. Changes in laboratory parameters without regard to drug relationship are:
Hepatic- elevated SGPT(ALT), SGOT(AST), GGT, alkaline phosphates. LDH, bilirubin.
Hematologic- decreased WBC, platelet count, elevated prothrombin.
Renal- elevated BUN, serum creatinine.
Immunocompromised Pediatric Patients: See the package insert.
-
អន្តរប្រតិកម្ម
Data available to date indicate clarithromycin is metabolized primarily by the hepatic CYP3A isozyme. This is an important mechanism determining many drug interactions.
The metabolism of other drugs by this system may be inhibited by concomitant administration with clarithromycin and may be associated with elevations in serum levels of drug classes known or suspected to be metabolized by the same CYP450 and CYP3A isozyme.
Other Drug Interactions:
- Elevated digoxin serum concentrations have been reported in patients receiving clarithromycin tablets and digoxin concomitantly. Monitoring of serum digoxin levels should be considered.
- There have been post-marketed reports of torsades de pointes occurring with concurrent use of clarithromycin and quinidine or disopyramide. Serum levels of these medications should be monitored during clarithromycin therapy.
- Rhabdomyolysis coincident with the co-administration of clarithromycin and the HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, e.g., lovastatin and simvastatin, has rarely been reported.
Antiretroviral Drug Interactions (zidovudine, dideoxyinosine, ritonavir): See the package insert.
-
ស្ត្រីមានផ្ទៃពោះ និង ស្ត្រីបំបៅដោះកូន
Clarithromycin is excreted into human milk therefore clarithromycin should not be used during pregnancy and breast-feeding unless the potential benefit justifies a potential risk to the foetus.
If clarithromycin pediatric suspension is considered for patients of post-pubertal age the physician should carefully weigh the benefits against the risk when pregnancy is either suspected or confirmed.
-
ការប្រុងប្រយ័ត្នជាពិសេស
Special populations: Hepatic impairment, Renal impairment, Elderly subjects: See the package insert.
Patients with Mycobacterial Infections:
Steady-state concentrations of clarithromycin and 14-OH-clarithromycin observed following administration of usual doses to patients with HIV infections were similar to those observed in normal subjects. However, at the higher doses which may be required to treat mycobacterial infections, clarithromycin concentrations can be much higher than those observed at usual doses. In children with HIV infection taking 15-30mg/kg/day of clarithromycin in two divided doses, steady-state Cmax values generally ranged from 8-20mcg/mL.
However, Cmax values as high as 23mcg/mL have been observed in HIV-infected pediatric patients taking 30mg/kg/day in two divided doses as clarithromycin pediatric suspension. Elimination half-lives appeared to be lengthened at these higher doses as compared to that observed with usual doses in normal subjects. The higher plasma concentrations and longer elimination half-lives observed at these doses are consistent with the known nonlinearity in clarithromycin pharmacokinetics.
- Caution is required in patients with impaired renal or hepatic function and doses should be reduced in those with severe renal impairment.
- Caution should also be paid to the possibility of cross-resistance between clarithromycin and other macrolide drugs, as well as lincomycin and clindamycin.
- Pseudomembranous colitis has been reported with nearly all anti-bacterial agents, including macrolides, and may range in severity from mild to life threatening.
- Clarithromycin in combination with ranitidine bismuth citrate therapy should not be used in patients with a history of acute porphyria.
-
សកម្មភាពឱសថ
Clarithromycin exerts its antibacterial action by binding to the 50S ribosomal subunits of susceptible bacteria and suppresses protein synthesis.
Clarithromycin has demonstrated excellent in vitro activity against both standard strains of bacteria and clinical isolates. It is highly potent against a wide variety of aerobic and anaerobic gram-positive and gram-negative organisms. The minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of clarithromycin are generally one log2 dilution more potent than the MICs of erythromycin.
Clarithromycin is reported to be more active than erythromycin against susceptible streptococci and staphylococci in vitro, as well as against some other species including Moraxella catarrhalis (Branhamella catarrhalis), Legionella spp. Chlamydia trachomatis, and Ureaplasma urealyticum. Clarithromycin is reported to be more active than erythromycin or azithromycin against some mycobacteria, including Mycobacterium avium complex, and against M.leprae. It is reported to have some in vitro activity against cryptosporidia. The major metabolite 14-hydroxyclarithromycin, is also active, and may enhance the activity of clarithromycin has excellent activity against Legionella pneumophilla, and Mycoplasma pneumoniae. It is bactericidal to Helicobacter pylori; this activity of clarithromycin is greater at neutral pH than at acid pH. In vitro and in vivo data show that this antibiotic has activity against clinically significant mycobacterial species.
*ព័ត៌មានឱសថត្រូវបានរៀបរៀងដោយ អ៊ីម៉ាតុគឹ មេឌីក (ខេមបូឌា) ដោយផ្អែកលើប្រភពព័ត៌មានខាងក្រោម។ សម្រាប់ព័ត៌មានលម្អិត សូមស្វែងរកនៅក្នុងក្រដាសព័ត៌មាននៃឱសថនីមួយៗ ឬ សាកសួរទៅកាន់ក្រុមហ៊ុនឱសថឬតំណាងចែកចាយនៃឱសថនីមួយៗ។
ប្រភពព័ត៌មាន៖
- ក្រដាសព័ត៌មាននៃឱសថសម្រាប់អ្នកជំនាញវេជ្ជសាស្ត្រដែលប្រើប្រាស់នៅប្រទេសជប៉ុន (Pharmaceutical and Medical Devices Agency, Pmda): https://www.pmda.go.jp
- ព័ត៌មានសង្ខេបនៃឱសថសម្រាប់អ្នកជំងឺដែលប្រើប្រាស់នៅប្រទេសជប៉ុន: http://www.rad-ar.or.jp
